Spain’s Congress Approves Termination of Golden Visa Program
Key Takeaways:
- Spain’s Golden Visa program, which grants residency in exchange for significant investments, will be officially abolished following approval by the Spanish Congress.
- The program had been criticized for driving up real estate prices and contributing to a housing crisis, especially in major cities like Madrid and Barcelona.
- The termination follows an earlier veto by the Spanish Senate, with Congress voting 177 in favor and 170 against the measure.
- The decision reflects the Spanish government’s focus on addressing the housing affordability issue, prioritizing residents over foreign investors.
Introduction
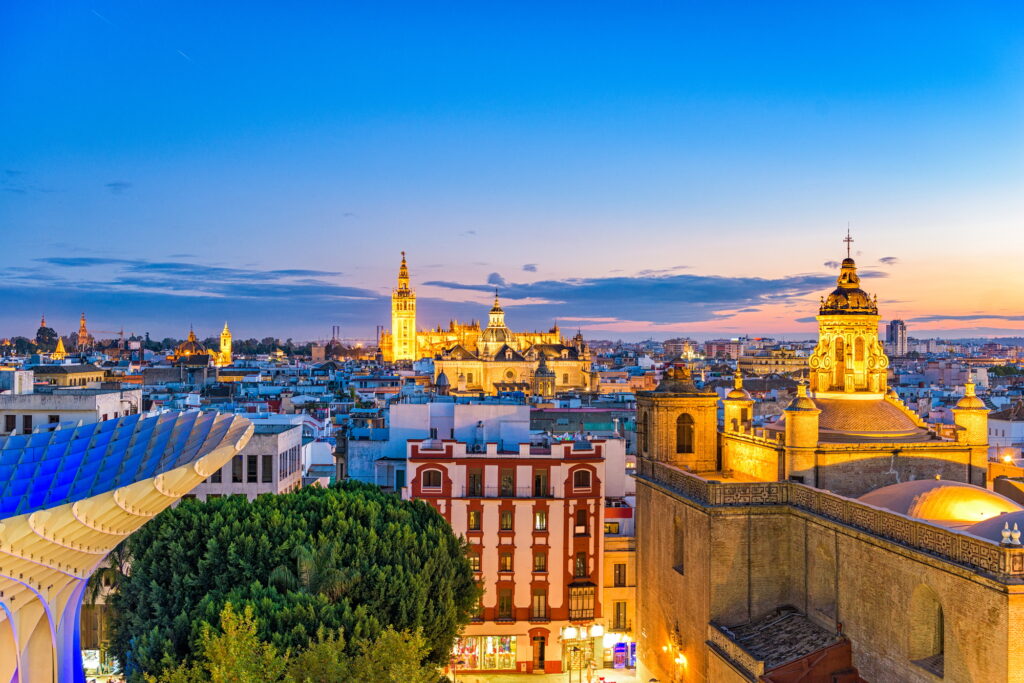
Spain’s Golden Visa program, which has been in place since 2013, allowed foreign nationals to gain residency by investing in real estate or other economic ventures, such as job creation or business investment. The program was particularly popular among wealthy investors seeking access to the European Union (EU), with Spain’s vibrant property market being a significant attraction. However, after years of debate and criticism, the Spanish Congress has passed a law to end the program, aiming to alleviate growing concerns over housing affordability and to curb speculative real estate investments.
The Golden Visa program was designed to bring in foreign capital, and it succeeded in attracting wealthy individuals to Spain. However, it faced increasing opposition due to its unintended effects on the housing market, particularly in urban centers where property prices surged as a result of foreign investments. By ending the program, the Spanish government aims to focus on ensuring that housing remains affordable for its citizens and is not used as an asset for speculative purposes.
Details of the Reform
The Golden Visa program allowed investors who made a minimum of €500,000 in property investments or other qualified financial contributions to receive residency permits in Spain. Over the years, the program has attracted many high-net-worth individuals, particularly from China, Russia, and the Middle East. Many Golden Visa holders bought luxury properties in cities like Madrid, Barcelona, and coastal areas, adding to the demand for high-end real estate. This surge in demand contributed to rising property prices, making housing less affordable for locals.
Despite the program’s economic benefits—such as the influx of investment capital—the Spanish government began receiving increasing pressure from both local residents and advocacy groups who argued that the influx of foreign money was exacerbating Spain’s housing affordability crisis. In 2023, the government introduced a proposal to end the Golden Visa program, focusing instead on measures that would allow for a more equitable housing market and promote investment in areas that benefit local communities.
The Legislative Process
The proposal to end the Golden Visa program was met with mixed reactions in Spain’s political landscape. While some saw it as a necessary step to protect the housing market and prioritize the needs of local residents, others argued that the program had brought important economic benefits. After passing in the Spanish Congress, the proposal was sent to the Senate, where it was initially vetoed. However, the Spanish Congress overruled the Senate’s veto and passed the reform with 177 votes in favor and 170 votes against, signaling strong support for the policy shift.
Once the reform is officially published in the Official State Gazette, the Golden Visa program will be officially terminated. The Spanish government’s decision to proceed with the reform, despite opposition from some sectors, highlights its commitment to addressing long-standing issues in the housing sector, especially as Spain deals with an ongoing housing crisis affecting many of its major urban areas.
Economic and Social Impact
While the Golden Visa program was seen as a tool to boost foreign investment, the economic benefits were not without costs. The average investment per Golden Visa applicant was €657,204, and in 2024 alone, 780 visas were issued. This represented a significant flow of capital into the Spanish economy, particularly in the real estate sector, as foreign buyers were able to purchase high-value properties across the country.
However, the broader social impact of this investment has been more controversial. Critics argued that the program contributed to skyrocketing property prices in major cities, pricing out local residents and creating an environment where housing became increasingly unaffordable for ordinary Spaniards. In areas like Barcelona, real estate prices rose dramatically in part due to the influx of foreign buyers, leading to tensions between locals and investors.
In addition to the housing affordability issue, there were concerns that the program did not necessarily lead to the creation of jobs or long-term economic benefits for Spain. The focus on real estate as a key investment for the Golden Visa meant that other sectors, such as tech or research, received less attention. By terminating the program, the government hopes to reallocate resources and focus on more sustainable economic growth that benefits the population at large.
Global Reactions and Future Outlook
The decision to abolish the Golden Visa program will likely have ripple effects beyond Spain’s borders. Other European countries that operate similar programs, such as Portugal and Greece, may face increased scrutiny regarding the social and economic impacts of residency-by-investment schemes. These programs have been criticized for encouraging speculative investments in real estate, which can lead to gentrification and displacement of local populations.
For Spain, the immediate impact of ending the Golden Visa program will likely be felt in the real estate market, where demand from foreign buyers could decrease. However, the government hopes that this shift will encourage investment in other sectors, such as green energy, technology, and sustainable infrastructure. By focusing on industries that benefit local communities, Spain aims to foster a more inclusive and sustainable economy.
Conclusion
Spain’s decision to terminate the Golden Visa program marks a significant shift in its immigration and housing policies. While the program brought foreign investment to the country, it also contributed to rising property prices and affordability issues. With the new reforms, the Spanish government is prioritizing housing accessibility for local residents and moving towards a more sustainable and inclusive economic model. As Spain continues to face challenges in balancing economic growth with social equity, the termination of the Golden Visa program is part of a broader effort to address the needs of its citizens and ensure a fairer distribution of resources.
#